How to Prevent Cyber Attacks Before They Happen: The Essential Checklist
Strengthen your defenses with this 12-step proactive cybersecurity checklist. Learn essential prevention measures to stop cyber attacks, ransomware, and supply chain threats before they strike.

In 2025, cyber attacks turned out to be one of the most urgent problems concerning companies and people. The hackers are using more and more advanced methods, and thus the frequency of the supply-chain attacks has doubled. The question is not anymore if your business will be targeted, but rather when. At least, there is a silver lining in the fact that proactive security measures can prevent the vast majority of cyber attacks. This exhaustive checklist gives you the vital actions to take in order to strengthen your defenses and intercept threats before they ever exist.
Understanding Proactive Cybersecurity
Proactive cybersecurity means dealing with any possible cyber threats at their roots by making a kill of them before they manifest, instead of doing the latter after the incident occurs. This very forward-looking approach turns out to be of great importance in present-day risk management since it gives organizations the possibility to outsmart the imminent dangers, which will in turn decrease the number of data leakages and thus, allow them to be always available. Through the constant testing of the security measures and the installation of security validation processes that are automatically done, the companies will be able to reinforce their walls against the changing threats.
The Complete Proactive Cybersecurity Prevention Checklist: 12 Essential Steps to Stop Cyber Attacks in 2025
1. Implement Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication
Passwords still continue to be one of the most vulnerable points in the area of cybersecurity. For better protection, the use of a complex mixture of letters, numbers, and special characters is suggested, with passwords having a length of 12 to 16 characters. Password managers can create, keep safe, and organize complicated passwords, thus allowing users to forget about the hassle of remembering various logins.
Multi-factor authentication strengthens security further by imposing extra verification apart from the passwords. MFA requires that users provide two or more types of verification before they are allowed in, usually including something the user knows (password), something the user has (hardware token or smartphone), and something the user has (biometrics). Many cyber insurers now consider MFA to be the minimum standard.
2. Keep All Software and Systems Updated
Updating software and operating systems is one of the crucial cybersecurity maintenance tasks, and it is also the first line of defense in preventing cyber-attacks. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in the software, and the updates usually come with the necessary security patches. In 2023, the unpatched vulnerability was the major reason for cybercrime in 23% of the organizations globally.
The on-off updates for the operating systems, applications, and security tools will make the devices and the systems less vulnerable to exploits. This allows the devices and systems to receive the latest security patches as soon as they are available without any manual intervention. The regular scanning for vulnerabilities will help in finding the weak points that require immediate remediation.
3. Deploy Comprehensive Endpoint Protection
Endpoints-including workstations, phones, and servers-are the main targets for attacks. Reputable antivirus, anti-spyware, and anti-malware tools should be used to scan and block the malware. Schedule scans on a regular basis to discover and eliminate dangers and have continuous updates for malware patterns.
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) software is a solution that constantly monitors, identifies, investigates, and responds to advanced endpoint threats. Even though traditional antivirus software helps secure endpoints by detecting known malware, it is very often not enough to deal with the new types of threats. Cyber insurance companies usually ask EDR to be included in the cyber incident response plans of organizations.
4. Establish Robust Firewall and Network Security
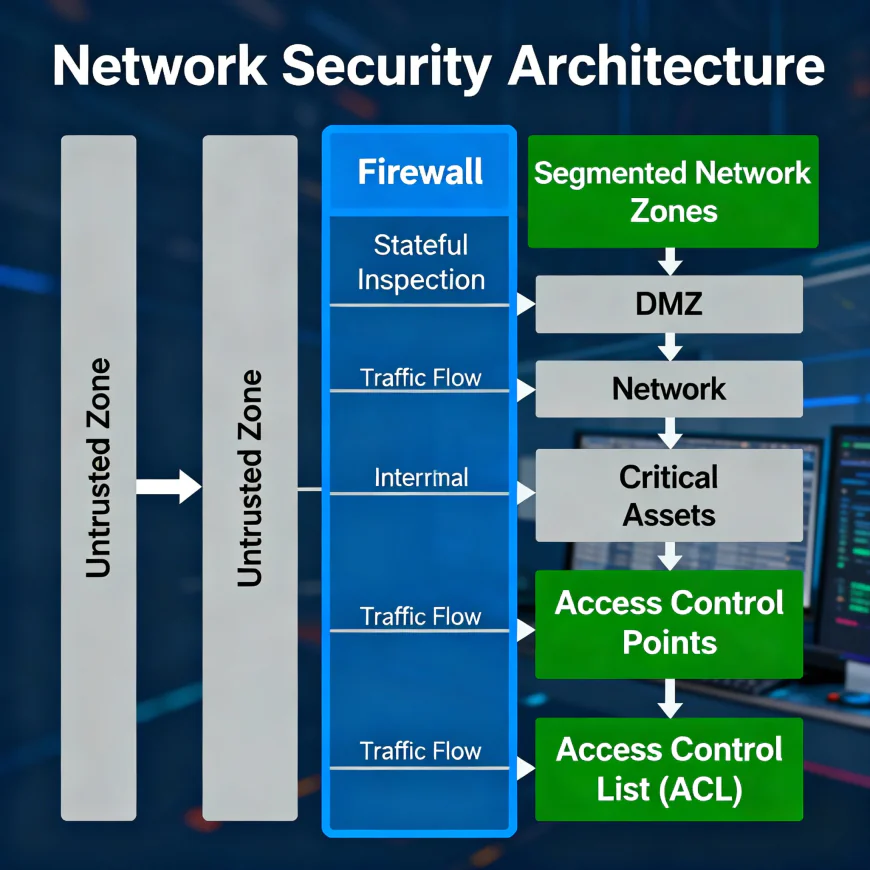
Firewalls provide a means of protection by restricting unauthorized access to the network through the monitoring of the traffic in and out of the network. Firewalls perform the role of gatekeepers by regulating the flow of data through the network according to the pre-set security rules and thus forming a wall between the internal networks that are regarded as safe and the external ones that are not.
The method of network segmentation involves breaking down a large network into smaller and isolated portions, called subnets, in order to enhance security, improve organization, and increase performance. The approach taken here restricts the movement of cyber attackers who have found their way into the network. In the event of a security breach, segmentation will allow the intruders only to be in the compromised area, thus they will have limited access, and this will reduce the chances of the whole network being impacted.
Configure your WiFi with WPA3 encryption and change the default router password. Avoid using public WiFi for sensitive transactions unless using a private, secured VPN.
5. Encrypt Sensitive Data

Encryption works by changing the form of the data in such a way that unauthorized users are unable to use it even if it has been cracked open. This is the case for data that is being transmitted as well as for the data that is already stored, which includes emails, files, and databases.
An organization has to use AES-256 (Advanced Encryption Standard with 256-bit keys) as the minimum standard for encrypted data that is set aside. Companies are required to secure their online data through secure channels such as TLS 1.3 (Transport Layer Security). Organizations will need to use secure hardware such as Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) to take care of the encryption keys. Such hardware shields against both extraction and disruption of the key.
6. Conduct Regular Employee Security Training
With the use of new security techniques, the human factor still comes to the forefront as the most frequent cause of security breaches, with the most recent statistics revealing that employee carelessness was responsible for 95% of all data breaches. The appropriate training for end-users not only imparts knowledge to the employees but also creates a human firewall that is capable of repelling intruders at the very initial stage of their attack.
Train your employees regularly on phishing, social engineering, and security awareness so that they can identify potential threats. The new curriculum should cover education, practice, and reinforcement, with the inclusion of short scenario-based modules, realistic simulations styled after the current threat patterns, and periodic refreshers to cover the new risks that may have developed.
Incorporate the essentials of employee training focusing on critical data security threats like email phishing, counterfeit websites, insecure document sharing, and the dangers of using non-secured public Wi-Fi. Comply with the requirement of annual training and at the same time, enhance the learning process through regular monthly simulations or quarterly refreshers.
7. Implement Access Controls and Least Privilege Principles
The principle of least privilege should be applied, guaranteeing that users get only the access they need for their job duties. Utilize role-based access control (RBAC) to administer and restrict access to sensitive areas. RBAC distributes permissions as per the established roles across the organization, making access management smoother and more consistent.
Conduct periodic reviews of user rights in order to make sure that employees switching roles give up the privileges of their former roles. Access control prevents unauthorized users from getting into data and resources, thus only allowing authenticated users to have access.
8. Establish Regular Data Backup Procedures

In case of a cybersecurity incident like a ransomware attack, it is necessary to have backups of important data. Keep copies of essential data in a safe, off-site, or cloud-based storage system. Have frequent backups of systems, preferably automated, to make sure data can be restored rapidly.
Test the restoration process periodically to verify that the backup process is functioning properly. Cyber insurance companies often impose certain backup standards on businesses, such as having established backup procedures, making offline backups, or using an alternative backup method.
9. Develop and Test an Incident Response Plan
Develop a documented plan for dealing with cybersecurity incidents, such as data breaches or ransomware attacks. An incident response plan is a documented strategy that explains how your company will spot, react to, and heal from cyber security incidents.
In case of a cyber attack on your network, it should be evident who will activate the response plan. The incident response plan must incorporate the individuals who will be responsible for the incident response, stating their position and providing their contact details.
Constantly practice and refresh the incident response plan to enhance preparedness. It is a document that lives through your organization and has to be checked and updated whenever there is a change in your environment or at least once a year.
10. Implement Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) refers to a security approach that requires continuous verification of all users and devices no matter their location. Unlike traditional models that placed trust in internal users first, Zero Trust treats all access attempts to the resource as potentially unfriendly-the network included.
Implementing least privilege access is the procedure of providing users only the minimum permissions required for them to perform their tasks. Rather than granting users access to the entire network, it is better to consider the smaller, secure zones created by micro-segmentation as the areas for resource isolation and damage control in case of a breach. Multi-factor authentication should be put in place, wherein users are confirmed through at least two or more different methods of authentication before being allowed entry.
11. Secure Cloud Environments and Supply Chain
Centralized logging should be enabled to make the logs of all the cloud services and resources consolidated into one central place. It is recommended to set up alerts for activities that might be considered suspicious, such as unusual logins or network traffic. Least privilege principle should be applied to firewalls and security groups configuration to manage the traffic in and out.
Data in the cloud must always be encrypted, and this should be the default state. It is very important to know the shared responsibility model in cloud security. Create full visibility in your operations and endpoints, which includes user activity, resource usage, and security event understanding.
Since April 2025, supply chain attacks have increased twofold, and the average number of such attacks per month is 26. Determine the security posture of third-party vendors and partners before you work with them. Vendors, contracts, and SLAs should include security requirements, and access to sensitive data and systems by vendors should be monitored and audited.
12. Conduct Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits help in finding weaknesses and assessing how effective the put measures are. An exhaustive cybersecurity audit checklist should be used to scrutinize your organization's security posture and rectify the vulnerabilities discovered at once.
Penetration testing is a very effective security measure that involves hiring professional and friendly hackers to deliberately attempt to penetrate your company's defenses. This approach discovers weak spots and security holes in the network, thereby, strengthening the overall security posture.
Install security monitoring systems for monitoring and capturing any suspicious activities like strange logins or data transfers. Proactive monitoring means that your company is always on the lookout for the threats that are about to happen.
Building a Culture of Security
Making sure of safety measures is a way to beat the problem before it comes instead of facing the very costly loss of recovery. You need to think of this as an essential checklist where you build up several layers to fight off the attacks and thus your attack surface shrinks considerably, so that it becomes much harder for the hackers to win.
Keep in mind that the process of securing the IT realm will never stop; it would be more of a cycle where, after every completion, you would have to go through all stages. Securing the measures, in the first place, will be decisive since you would be able then to block cyber threats before they get the chance to strike, thus making your company immune to future threats etc. a saving in treatment has always been as the saying goes "prevention is better than cure".
Making the digital world safer for yourselves is the only way to go starting from now.