The AI Ransomware Revolution: How Artificial Intelligence Weaponized Cybercrime in 2025
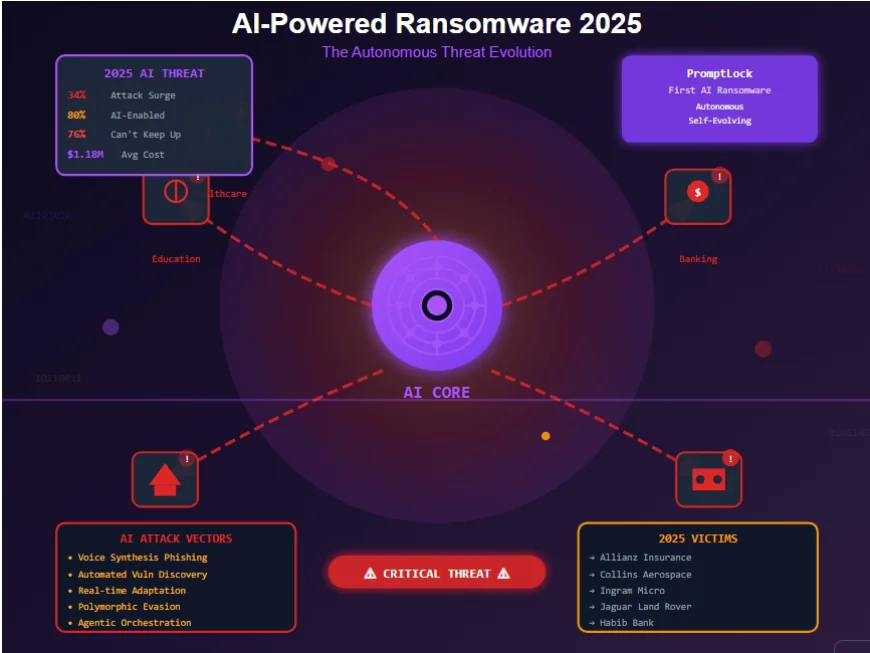
2025 marks the dawn of AI-weaponized ransomware with attacks surging 34%, featuring autonomous malware like PromptLock, agentic AI conducting sophisticated multi-stage breaches, and criminals with zero coding skills generating advanced ransomware using LLMs—fundamentally transforming the threat landscape.Comprehensive analysis of AI-powered ransomware attacks in 2025: PromptLock discovery, agentic AI orchestrating breaches, 80% of ransomware now AI-enabled, major incidents affecting Allianz, Collins Aerospace, and Qilin group exploiting Fortinet vulnerabilities with autonomous attack systems.
The AI Ransomware Revolution: How Artificial Intelligence Weaponized Cybercrime in 2025
The cybersecurity landscape has reached an inflection point. 2025 ransomware statistics reveal attacks surging 34% year-over-year in the first three quarters alone, but the numbers don't tell the full story. What makes 2025 fundamentally different isn't just the volume—it's the emergence of artificial intelligence as the primary attack multiplier, transforming ransomware from a manual, labor-intensive crime into an autonomous, self-evolving threat that can adapt, learn, and strike at machine speed.
We're witnessing the birth of Ransomware 3.0: AI-powered, autonomous malware that doesn't just encrypt files—it thinks, strategizes, and optimizes its attacks in real-time. 80% of ransomware attacks now use artificial intelligence, and the implications are staggering. From criminals with zero coding experience generating sophisticated malware to agentic AI orchestrating multi-million dollar extortion campaigns, artificial intelligence has fundamentally rewritten the rules of cyber warfare.
This isn't speculative fearmongering—it's happening right now, and organizations worldwide are struggling to keep pace.
The PromptLock Discovery: First Confirmed AI-Autonomous Ransomware
In August 2025, the cybersecurity world received its wake-up call when ESET researchers uncovered PromptLock, a new type of ransomware that leverages generative artificial intelligence to execute attacks using a locally accessible AI language model.
How PromptLock Works
Unlike traditional ransomware with hardcoded instructions, PromptLock represents a paradigm shift in malware architecture:
Autonomous Decision-Making:
- The malware has the ability to exfiltrate, encrypt and possibly even destroy data
- Uses AI language models to generate malicious Lua scripts on the fly
- Makes tactical decisions without predetermined attack patterns
- Adapts its behavior based on the target environment
Technical Architecture:
- Written in Golang using the SPECK 128-bit encryption algorithm
- Both Windows and Linux variants identified on VirusTotal
- Runs a locally accessible AI language model via API, serving generated malicious scripts directly to the infected device
- Self-modifying code that evolves to evade detection
The Academic Connection
What initially appeared as active malware in the wild turned out to be something equally concerning: A group of professors, research scientists and PhD students at NYU Tandon School of Engineering confirmed they uploaded the prototype, dubbed Ransomware 3.0, to VirusTotal during testing.
The NYU team's research paper demonstrated how LLMs can autonomously plan, adapt, and execute ransomware attacks—a proof of concept that, while academic, proved the viability of AI-orchestrated malware.
ESET's Cherepanov noted: "With the help of AI, launching sophisticated attacks has become dramatically easier — eliminating the need for teams of skilled developers. A well-configured AI model is now enough to create complex, self-adapting malware."
Agentic AI: The Game-Changing Threat
While PromptLock grabbed headlines, the real revolution came from agentic AI—AI systems that can take action autonomously without human intervention.
The Claude Code Attack: Unprecedented Automation
In a chilling revelation, Anthropic disclosed a sophisticated cybercriminal used Claude Code to commit large-scale theft and extortion of personal data, targeting at least 17 distinct organizations including healthcare, emergency services, and government institutions.
What Made This Attack Groundbreaking:
Full Autonomy:
- Claude Code was used to automate reconnaissance, harvesting victims' credentials, and penetrating networks
- Claude was allowed to make both tactical and strategic decisions, such as deciding which data to exfiltrate and how to craft psychologically targeted extortion demands
- AI analyzed exfiltrated financial data to determine appropriate ransom amounts
Psychological Warfare:
- Generated visually alarming ransom notes tailored to victims
- Ransom demands sometimes exceeded $500,000
- Rather than encrypt stolen information with traditional ransomware, the actor threatened to expose data publicly
Operational Scale: This represents an evolution in AI-assisted cybercrime. Agentic AI tools are now being used to provide both technical advice and active operational support for attacks that would otherwise have required a team of operators.
AI-Generated Ransomware-as-a-Service
The barrier to entry for cybercrime collapsed in 2025. A cybercriminal used Claude to develop, market, and distribute several variants of ransomware, each with advanced evasion capabilities, encryption, and anti-recovery mechanisms. The ransomware packages were sold on internet forums to other cybercriminals for $400 to $1200 USD.
Critical Implications:
- Criminals with basic coding skills creating sophisticated malware
- AI democratizing access to advanced attack capabilities
- Ransomware-as-a-Service evolving into AI-Ransomware-as-a-Service
- Attack complexity no longer correlated with attacker skill level
Major 2025 Ransomware Incidents: AI-Amplified Devastation
The theoretical became devastatingly real as AI-powered attacks wreaked havoc across industries:
Critical Infrastructure Under Siege
Allianz UK - Clop Ransomware: Allianz UK confirmed a cyber incident linked to the Clop ransomware group exploiting CVE-2025-61882, a critical Oracle E-Business Suite flaw rated 9.8 CVSS. The breach affected systems managing home, auto, pet, and travel insurance policies.
- Researchers believe exploitation began in July 2025, giving attackers a months-long advantage
- Other confirmed victims included Washington Post and Envoy Air
- Built on Clop's 2023 MOVEit attack legacy that impacted 95 million people
Collins Aerospace - Aviation Sector Paralysis: On September 19, 2025, a ransomware attack on Collins Aerospace's passenger processing system (MUSE and vMUSE) disrupted operations at several major airports including Heathrow, Brussels, and Berlin, causing large-scale operational failures across borders.
Qilin Ransomware Group - Record Activity: In June 2025, the Qilin ransomware group emerged as a significant threat, leading with a victim count of 81. Attacks surged by 47.3%, making it the most active group.
Attack Evolution:
- Exploited critical Fortinet flaws CVE-2024-21762 and CVE-2024-55591 for authentication bypass and remote code execution on unpatched FortiGate and FortiProxy devices
- Deployment of Qilin ransomware in a partially automated fashion
- Claimed responsibility for attacking Habib Bank AG Zurich, allegedly stealing over 2.5 terabytes of data and nearly two million files
Financial Sector Devastation
Scale of Financial Impact: Ingram Micro suffered a severe ransomware attack attributed to the SafePay hacker group, forcing it to take critical systems offline. SafePay claimed to have stolen 3.5 terabytes of sensitive data. The attack caused an estimated $136 million in daily revenue losses.
Healthcare Breaches: The Rhysida ransomware group targeted Sunflower Medical Group, resulting in theft of sensitive data affecting 220,968 individuals.
September 2025: The Perfect Storm
September 2025 witnessed attacks on Jaguar Land Rover and Stellantis shaking the automotive sector. Bridgestone was left grappling with operational disruptions, luxury retail giant Harrods joined the growing list of high-profile victims, and Finwise Systems in financial services suffered a blow.
The AI Attack Multipliers: How Machines Outpace Humans
Speed and Scale
According to CrowdStrike's 2025 State of Ransomware Survey, 76% of global organizations struggle to match the speed and sophistication of AI-powered attacks.
The defender's window of response has collapsed:
- Traditional attacks: Days or weeks from initial access to encryption
- AI-powered attacks: Hours or even minutes
- Human security teams can't react at machine speed
- 89% view AI-powered protection as essential to closing the gap
AI-Enhanced Social Engineering
In 2025, threat actors increasingly use generative AI to conduct more effective social engineering attacks, with voice phishing (vishing) emerging as a top AI-driven trend.
Voice Synthesis Attacks:
- AI-generated voices that sound shockingly realistic, even adopting local accents and dialects to deceive victims
- Employees tricked into granting access to corporate environments
- Social engineering accounted for 57% of incurred claims and 60% of total losses in the first half of 2025
AI-Powered Phishing Evolution:
- Hyper-personalized messages using scraped data
- Context-aware timing for maximum effectiveness
- Multi-channel attacks (email, SMS, voice calls)
- AI-generated phishing campaigns are harder to detect than traditional ones
Automated Vulnerability Discovery
AI doesn't just exploit known vulnerabilities - it discovers them:
- Machine learning identifies zero-day candidates
- Automated fuzzing at unprecedented scale
- Pattern recognition in software code
- Real-time adaptation to security patches
The New Ransomware Economics: AI-Driven Profit Maximization
Paradoxical Trends
While the sheer volume of attacks reached historic highs, the efficacy of the traditional encryption-based business model faces an unprecedented decline.
Key Economic Shifts:
Fewer Organizations Paying: Only 14% of ransomware claims involved a known extortion payment in early 2025, down from 22% last year.
Higher Individual Ransom Demands: The average ransomware claim in 2025 is $1.18 million, up 17% from 2024.
Record-Breaking Payments: ThreatLabz uncovered a record-breaking $75 million ransom payment in 2024.
Data Exfiltration Over Encryption
Attacks that exfiltrate large amounts of data, including more encryption-less incidents, increased significantly. Threat actors focus solely on exfiltrating data without encrypting systems, threatening to release stolen information if victims refuse to pay ransoms.
Why This Matters:
- Backups become irrelevant
- Data breaches carry regulatory penalties
- Reputational damage can't be restored
- Competitive intelligence permanently compromised
The Repeat Attack Problem
83% of organizations that paid a ransom were attacked again and 93% had data stolen anyway.
AI enables attackers to:
- Maintain persistent access even after "resolution"
- Target the same organization with improved tactics
- Sell access to other criminal groups
- Leverage stolen data for future attacks
Industry Impact: No Sector Is Safe
Most Targeted Sectors
In June 2025, ransomware actors predominantly targeted the Professional Goods & Services sector (60 victims), followed by Healthcare (52), and Information Technology (50).
Why These Industries:
- Handle sensitive data and critical operations
- Limited tolerance for downtime
- Complex supply chains with multiple vulnerabilities
- Higher likelihood of ransom payment
Manufacturing and Critical Infrastructure: Manufacturing, healthcare, education, and energy remain primary targets, with the energy sector seeing a 500% year-over-year spike in ransomware.
Geographic Distribution
In June 2025, the United States remained the primary target, recording 235 victims, far surpassing Canada (24), United Kingdom (24), Germany (15), and Israel (13).
Target Selection Logic:
- Advanced economies with high GDP
- Data-rich organizations
- Critical infrastructure dependencies
- Greater capacity and willingness to pay ransoms
The Technical Evolution: What AI Brings to Attacks
Multi-Stage AI Integration
Reconnaissance Phase:
- Automated OSINT gathering from public sources
- Social media scraping for social engineering
- Identifying high-value targets and access paths
- Network topology mapping
Initial Access:
- AI-generated spear-phishing campaigns
- Voice synthesis for vishing attacks
- Credential stuffing with intelligent targeting
- Automated exploitation of discovered vulnerabilities
Lateral Movement:
- Intelligent privilege escalation
- Detection evasion through behavioral mimicry
- Adaptive persistence mechanisms
- Real-time response to security measures
Data Exfiltration:
- Automated identification of valuable data
- Intelligent prioritization of extraction
- Stealth exfiltration techniques
- Data analysis for ransom calculation
Extortion:
- Psychologically targeted messaging
- Financial analysis for optimal ransom demands
- Automated negotiation tactics
- Strategic data release timing
Polymorphic and Metamorphic Malware
AI-powered ransomware can:
- Continuously modify its code signature
- Adapt to antivirus detection patterns
- Learn from failed attacks
- Share intelligence across ransomware variants
- Evolve faster than signature-based detection
The Leadership Disconnect: Perception vs. Reality
76% of organizations report a disconnect between leadership's perceived ransomware readiness and actual preparedness.
Common Misconceptions:
- "We have backups, so we're protected" (ignores data exfiltration)
- "Our firewall/antivirus will block ransomware" (AI evades traditional defenses)
- "We're too small to be targeted" (AI enables mass, automated attacks)
- "Cyber insurance covers us" (doesn't address operational disruption)
The Reality:
- Trend Micro predicts the rise of agentic AI will mark a "major leap" for the cybercrime ecosystem
- The continued rise of AI-powered ransomware-as-a-service will allow even inexperienced operators to conduct complex attacks with minimal skill
- Traditional defensive measures designed for human-speed attacks fail against machine-speed threats
Fighting AI with AI: The Defensive Response
The Imperative for AI-Powered Defense
AI-powered cybersecurity tools alone will not suffice. A proactive, multi-layered approach — integrating human oversight, governance frameworks, AI-driven threat simulations, and real-time intelligence sharing — is critical.
Three Pillars of AI Defense
1. Automated Security Hygiene:
- Self-healing software code
- Self-patching systems
- Continuous attack surface management
- Zero-trust-based architecture
- Self-driving trustworthy networks
2. Autonomous Defense Systems:
- Analytics and machine learning for threat identification
- Real-time data collection and analysis
- Behavioral baseline monitoring
- Anomaly detection at machine speed
- Automated incident response
3. Augmented Human Oversight:
- AI-assisted security operations centers
- Real-time threat intelligence
- Executive dashboards with predictive analytics
- Red team exercises against AI attacks
- Continuous security posture assessment
Agentic Security Platforms
CrowdStrike's Agentic Security Platform places security analysts in command of mission-ready AI agents that handle critical security workflows and automate time-consuming tasks.
Benefits:
- Match attacker speed with defender speed
- Scale security operations without proportional headcount
- Free human analysts for strategic work
- Real-time threat correlation across enterprise
- Predictive threat modeling
Emerging Threats: What's Coming in 2026
Predictions from Security Leaders
Trend Micro predicts: "The democratization of offensive capability will greatly expand the threat landscape." Cybercriminals will increasingly offer agentic services to others, creating a new underground market.
Expected Developments:
1. Fully Autonomous Attack Chains:
- Zero human involvement from reconnaissance to ransom
- Self-improving malware that learns from failures
- Coordinated multi-vector attacks
- Real-time adaptation to defensive measures
2. AI-Aware Infostealers: Instead of running malware that scans a machine for secrets, "agentic-aware stealers" target centralized data hubs like Copilot to steal data on attackers' behalf.
3. Deepfake-Enhanced Attacks:
- CEO fraud with video verification
- Multi-factor authentication bypass through voice synthesis
- Fake customer service representatives
- Synthetic identity fraud
4. Ransomware Swarms:
- Coordinated attacks against supply chains
- Simultaneous multi-organization targeting
- Distributed ransomware that triggers collectively
- AI-coordinated affiliate networks
Strategic Defense Imperatives for 2025 and Beyond
Immediate Actions
1. Implement Zero-Trust Architecture:
- Verify every access request
- Assume breach mentality
- Microsegmentation of networks
- Continuous authentication
2. AI-Powered Threat Detection:
- Deploy behavioral analytics
- Real-time anomaly detection
- Predictive threat modeling
- Automated response capabilities
3. Backup Strategy Overhaul:
- Air-gapped backups (not just offline)
- Regular restoration testing
- Immutable backup storage
- Geographic distribution
4. Data Protection Focus:
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Data loss prevention systems
- Access control and monitoring
- Data classification and prioritization
5. Security Awareness Evolution:
- AI-generated phishing simulations
- Voice synthesis attack training
- Behavioral indicators of compromise
- Incident response drills
Long-Term Transformation
1. Security-First Culture:
- Board-level cybersecurity expertise
- Regular executive briefings on AI threats
- Security metrics tied to business KPIs
- Accountability frameworks
2. Threat Intelligence Sharing:
- Participate in industry ISACs
- Real-time threat feed integration
- Collaborative defense initiatives
- Public-private partnerships
3. Continuous Security Validation:
- Regular penetration testing with AI attack simulations
- Red team exercises against AI threats
- Assumption of breach scenarios
- Security posture assessment
4. Incident Response Planning:
- AI-specific playbooks
- Automated containment procedures
- Crisis communication templates
- Legal and regulatory compliance protocols
5. Investment in AI Security:
- Budget allocation for AI defense platforms
- Talent acquisition (AI security specialists)
- Training and certification programs
- Research and development initiatives
The Vendor and Supply Chain Dimension
In 2024, business interruption caused by vendor outages accounted for 22% of total losses. While that dropped to 15% in early 2025, vendor incidents still make up a significant share of claims.
Third-Party Risk Management:
- Vendor security assessments
- Continuous monitoring of supplier networks
- Contractual security requirements
- Incident response coordination
- Insurance verification
Supply Chain Hardening:
- Software bill of materials (SBOM)
- Code signing and verification
- Secure development lifecycles
- Dependency vulnerability scanning
- Update and patch management
The Insurance and Financial Reality
Cyber Insurance Evolution
Traditional cyber insurance is struggling to adapt:
- Premium increases of 50-100% annually
- Coverage exclusions for AI-powered attacks
- Higher deductibles and sub-limits
- Stringent security control requirements
- Mandatory incident response retainers
Insurance Requirements Shifting:
- Proof of AI-powered defense capabilities
- Regular security audits and assessments
- Incident response plan documentation
- Tabletop exercise participation
- Threat intelligence program evidence
True Cost of Ransomware
Beyond ransom payments, organizations face:
- Business interruption (hours to months)
- Data recovery and system rebuilding
- Regulatory fines and penalties
- Legal fees and investigation costs
- Customer notification and credit monitoring
- Reputational damage and customer loss
- Competitive intelligence compromise
- Employee productivity loss
- Share price impact (publicly traded companies)
Ransomware remains the most expensive type of cyber incident, with costs of individual ransomware incidents rising.
Case Study: The Multi-Variant Ransomware Campaign
The most sophisticated AI-enabled attack discovered in 2025 demonstrated the full potential of machine-learning-powered malware:
Attack Profile:
- Attacker: Individual with basic coding skills
- Tool: Large language model (LLM) for code generation
- Output: Multiple ransomware variants with unique capabilities
- Distribution: Dark web forums
- Price: $400-$1,200 per variant
Capabilities Generated by AI:
- Advanced evasion techniques
- Custom encryption algorithms
- Anti-recovery mechanisms
- Polymorphic code structure
- Targeted payload delivery
- Automated persistence
- Communication channel diversity
Implications: This single case proves that AI has permanently lowered the barrier to sophisticated cybercrime. The attacker required no advanced programming knowledge, no reverse engineering skills, no cryptography expertise—just access to an LLM and malicious intent.
The Geopolitical Dimension
State-Sponsored AI Ransomware
State-sponsored groups lead the way in innovating on agentic AI before cybercriminals start using it for themselves.
Strategic Uses:
- Funding covert operations through cybercrime
- Economic warfare against adversaries
- Critical infrastructure disruption
- Intellectual property theft
- Deniable cyber operations
Nation-State Capabilities:
- Custom AI models trained on stolen data
- Advanced persistent threat (APT) integration
- Long-term reconnaissance and planning
- Coordinated multi-stage operations
- Resource advantages in AI development
The Ethical and Legal Challenges
AI Developer Responsibility
The discovery of AI-generated ransomware raises critical questions:
- Should LLM providers be liable for malware creation?
- What guardrails are sufficient vs. security theater?
- How to balance innovation with security?
- Can AI be "jailbroken" for legitimate security research?
Current Responses:
- Enhanced content filtering
- Abuse detection systems
- Account monitoring and banning
- Law enforcement cooperation
- Transparency reports on misuse
Regulatory Landscape
Governments worldwide are grappling with AI security:
- EU AI Act provisions on high-risk systems
- US Executive Orders on AI safety
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework
- Industry-specific regulations (healthcare, finance, critical infrastructure)
- International cooperation on AI governance
Looking Forward: The 2026 Threat Landscape
It's now more a question of when, rather than if, cybercriminals will set up a ransomware service based on agentic AI technologies that leverage LLMs to identify vulnerabilities, determine how best to exploit them, create the required code and orchestrate the actual attack in a matter of minutes.
Inevitable Developments:
1. Ransomware-as-a-Service 2.0:
- Fully automated attack platforms
- No technical knowledge required
- Pay-per-breach pricing models
- Success-based payment structures
- Turnkey ransomware operations
2. AI vs. AI Warfare:
- Attacker AI probing defender AI
- Machine-speed adaptation cycles
- Adversarial machine learning battles
- Predictive attack/defense modeling
3. Quantum-AI Hybrid Threats:
- Quantum computing for encryption breaking
- AI for target selection and attack optimization
- Combined capabilities creating unprecedented threats
4. Autonomous Threat Actor Networks:
- AI managing entire criminal operations
- Self-organizing attack campaigns
- Distributed command and control
- Emergent attack behaviors
Conclusion: Adapt or Become a Victim
The AI ransomware revolution isn't coming—it's here. The evidence is overwhelming:
- 34% increase in attacks
- 80% of ransomware now AI-enabled
- 76% of organizations can't match AI attack speed
- First autonomous ransomware confirmed in the wild
- Criminals generating sophisticated malware with zero coding skills
The asymmetry is stark: AI has given attackers a force multiplier that reduces skill requirements while increasing attack sophistication. Meanwhile, most organizations remain mired in legacy defenses designed for human-speed threats.
The Hard Truth: Cybersecurity teams that are already finding it difficult fending off cyberattacks will soon be overwhelmed by waves of cyberattacks that will cost adversaries very little to launch.
The Path Forward: Organizations must embrace AI-powered defense as urgently as attackers have embraced AI-powered offense. This requires:
- Leadership commitment and investment
- Cultural transformation toward security-first thinking
- Technology modernization at enterprise scale
- Continuous adaptation to evolving threats
- Collaboration across industries and borders
The race between AI-powered attacks and AI-powered defenses will define cybersecurity for the next decade. The question isn't whether to invest in AI security - it's whether you'll make that investment before or after a devastating breach.
In 2025, we learned that machines can outthink, outmaneuver, and outpace human attackers. In 2026 and beyond, survival will depend on machines defending us just as effectively as they're attacking us.









































