Ethical Hacking Automation: Using Python and Bash - Scripts for scanning and reporting.
In the world of cybersecurity, speed and precision are critical. Ethical hacking automation leverages Python and Bash to scan networks, enumerate vulnerabilities, and generate actionable reports — all without manual intervention. This blog explores how security professionals can streamline penetration testing workflows, automate routine checks, and maintain ethical standards, ensuring faster detection and mitigation of potential threats.

Introduction
In modern cybersecurity, manual penetration testing is no longer sufficient. Threat landscapes evolve rapidly, and security teams require automation to keep up. Ethical hacking automation combines the power of Python scripting and Bash commands to automate vulnerability scanning, reconnaissance, and reporting.
By implementing automation, security professionals can save time, reduce human error, and focus on complex attack simulations, while maintaining ethical standards and compliance.
Why Automate Ethical Hacking?
Manual security assessments are time-consuming and prone to inconsistencies. Automation provides:
- Speed: Execute scans on multiple targets simultaneously.
- Consistency: Standardized scripts reduce human error.
- Integration: Automation pipelines can feed results into CI/CD or incident response systems.
- Scalability: Large networks or multiple environments can be scanned efficiently.
Python is ideal for building customizable scanners, parsing results, and generating reports, while Bash excels at chaining tools like nmap, curl, ssh, and system utilities to orchestrate the testing workflow.
Practical Automation Examples
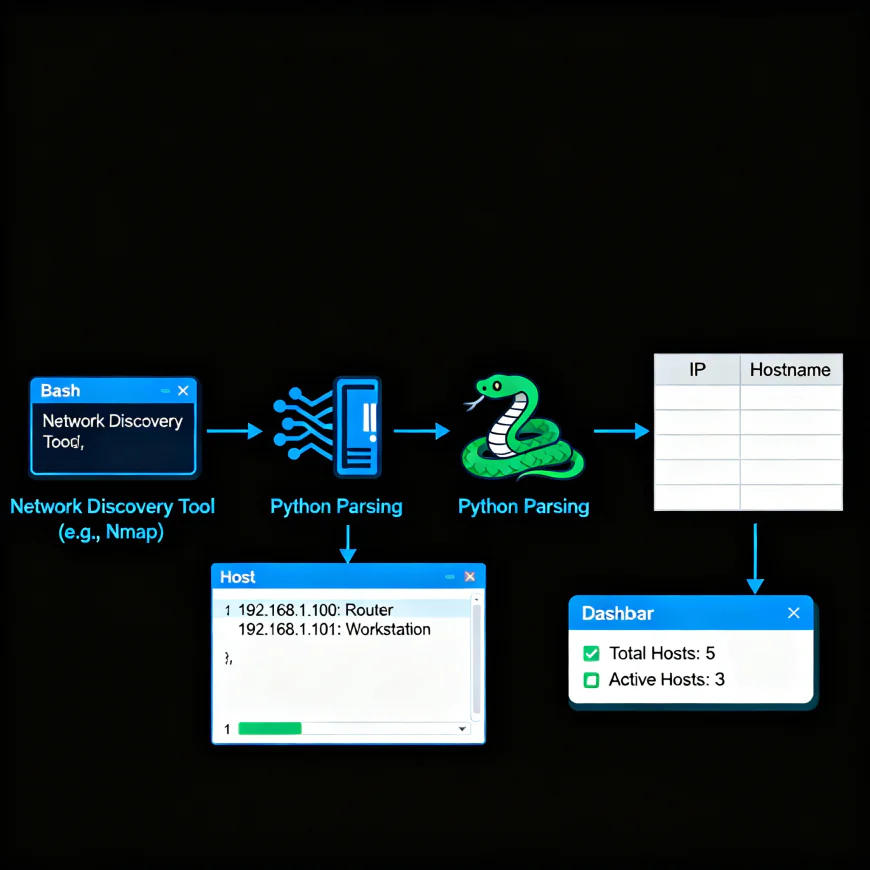
1. Network Reconnaissance
Using Python and Bash, you can automate host discovery:
#!/bin/bash
# Bash script: scan_network.sh
network="192.168.1.0/24"
nmap -sn $network -oG network_hosts.txt
echo "Active hosts saved in network_hosts.txt"
Then, Python can parse and analyze the results:
# Python script: analyze_hosts.py
import re
with open('network_hosts.txt') as f:
hosts = [line.split()[1] for line in f if re.search('Status: Up', line)]
print(f"Active hosts: {hosts}")
This combination allows automated discovery and reporting.
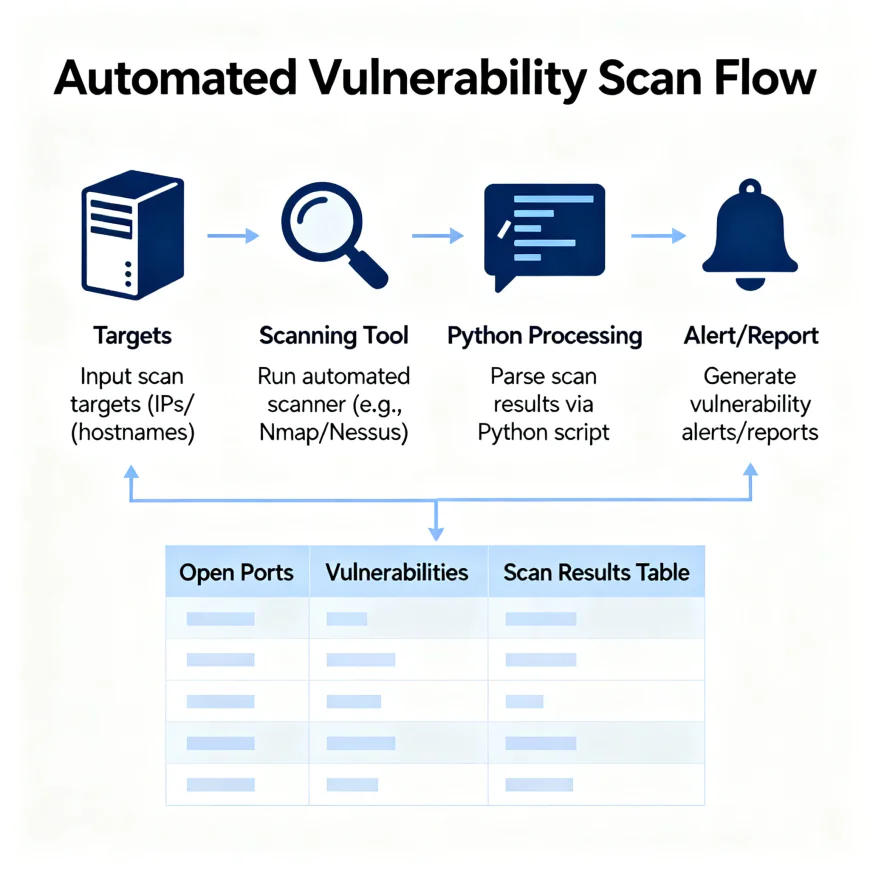
2. Vulnerability Scanning
Python can automate the execution of tools like Nikto, OpenVAS, or Nmap scripts:
import subprocess
targets = ["192.168.1.10", "192.168.1.15"]
for target in targets:
print(f"Scanning {target} for open ports...")
subprocess.run(["nmap", "-sV", target])
The script can be extended to log results, detect outdated software, or trigger alerts when high-severity vulnerabilities are found.
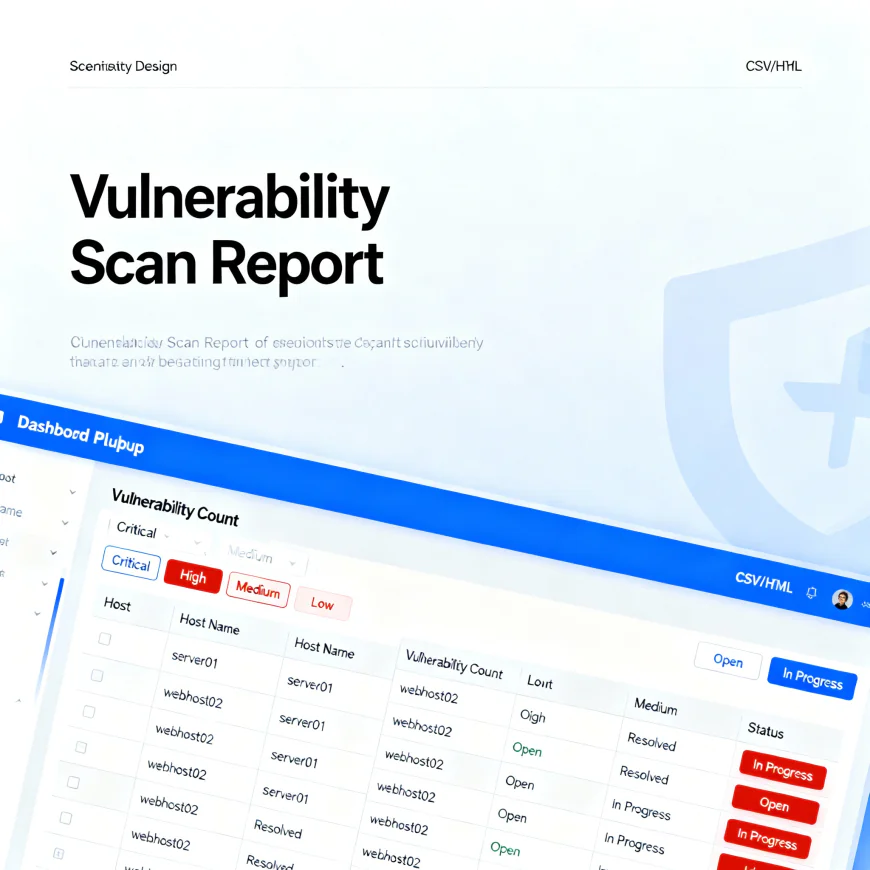
3. Automated Reporting
Generating readable, actionable reports is critical. Python’s pandas and Jinja2 libraries allow exporting results in HTML, PDF, or CSV formats:
import pandas as pd
# Sample scan results
data = {'Host': ['192.168.1.10', '192.168.1.15'],
'Open Ports': ['22, 80', '22, 443'],
'Vulnerabilities': ['None', 'Outdated SSL']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.to_csv('scan_report.csv', index=False)
print("Scan report generated: scan_report.csv")
You can also automate email notifications or push reports to a dashboard for team visibility.
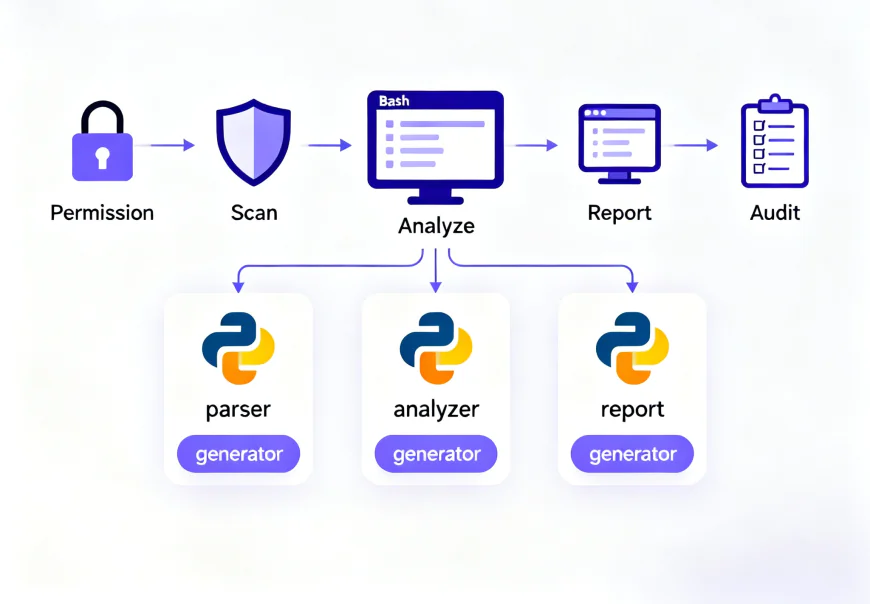
Best Practices for Ethical Hacking Automation
- Authorization is Key: Always have written permission before scanning or testing systems.
- Modular Scripts: Keep Bash and Python scripts modular for reusability.
- Logging & Audit Trails: Maintain logs for compliance and forensic purposes.
- Integrate with CI/CD: Security automation should be part of DevSecOps pipelines.
- Error Handling: Include proper exception handling to avoid script failures mid-scan.
Conclusion
Automation is transforming ethical hacking, making it faster, scalable, and more reliable. Combining Python and Bash allows security professionals to orchestrate complex testing workflows, perform continuous vulnerability monitoring, and deliver actionable insights — all while upholding ethical standards.
With careful design, ethical hacking automation scripts become an essential tool for proactive security and DevSecOps integration.








































