CCPA Compliance Guide for Businesses
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a landmark law that enhances data privacy rights for consumers, requiring businesses to be transparent about how they collect, use, and share personal information. Indian businesses serving California residents must comply to avoid severe fines and reputational damage.

Introduction
In the current generation of immense digital growth, data has become one of the most valuable possessions a business can have. Every click, every online purchase, and even simply filling out a form creates an enormous pool of personal information. Businesses use this to provide personalized service, targeted advertising and an improved customer experience, but there is also a potential dark side to the use of personal data. Privacy issues today, goes beyond just the theft of data - it encompasses how companies collect, store and share information about consumers. With nearly annual headlines of data breaches and privacy scandals there is an increased pressure from regulators all over the world to protect consumers against their misuse of data. One of the more notable laws surrounding consumer rights under CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). While this California based consumer privacy act is American, its reach is global. Indian businesses engaging with clients or consumers in California, or processing their processes as a function of web engagement requires an understanding of this law. A lack of understanding may result in fines of up to $7,500 a violation, legal action and potential damage to a company's reputation. This article will provide a complete guide to CCPA, its evolution and practical steps to avoid violations of compliance for Indian businesses.
What is CCPA?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) took effect on January 1, 2020. This is a historic and groundbreaking statute with the aim of enhancing data privacy rights for consumers. The CCPA empowers individuals to have more control over their personal information, while increasing businesses' accountability for the information they collect, use and share. Specifically, the CCPA empowers consumers by way of the following rights: Right to Know. Consumers can inquire about the personal information companies are collecting about them. Right to Delete. After making a request, consumers can have their personal information deleted from a company's records. Right to Opt-Out. Consumers can prevent companies from selling their personal information to third-parties. Right to Access. Consumers may access their personal information in a portable format. Overall, the CCPA requires companies to disclose how they use information and gives consumers the right to make informed decisions regarding their personal information. Although the CCPA is focused on California residents, digital businesses often conduct business across borders so an Indian company servicing an individual in California, is indirectly ensnared in the law. In fact, any website based in India, targeting California residents is governed by the CCPA.
Who Needs to Comply with CCPA?
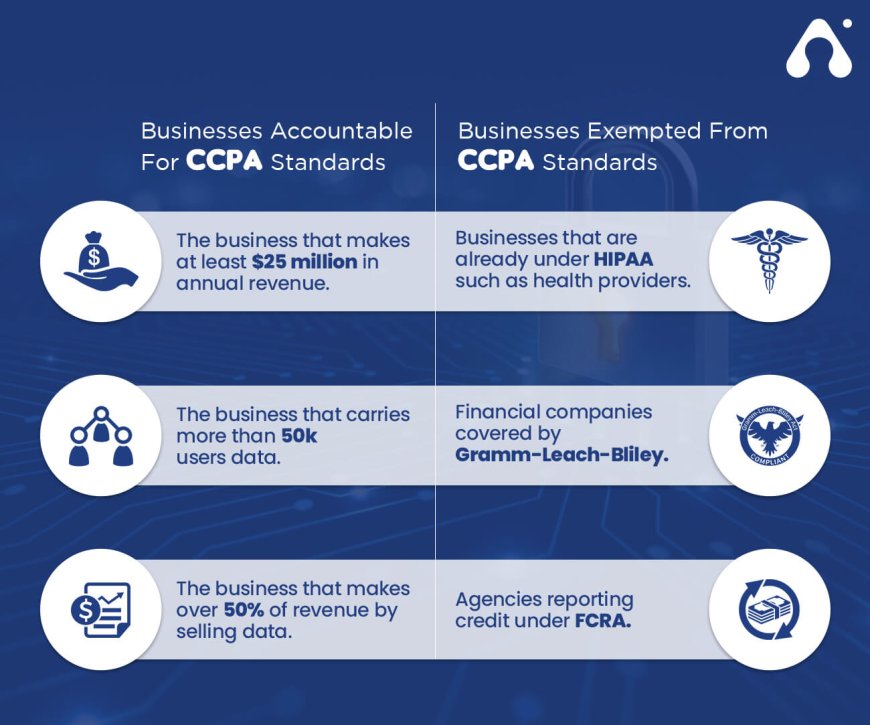
Not all businesses need to comply with CCPA. The law is tailored to organizations with substantial impact on consumer data. More specifically, it applies if the business meets at least one of the next three criteria: Annual gross revenues exceeding $25,000,000 Buying or selling or sharing personal information for 50,000 or more consumers in a calendar year Deriving more than 50% of annual revenues from the selling of consumer personal information Indian businesses including very small start-ups may also fall within the ambit of the law, even if the business is small, if the startup is doing business in the US market and is collecting data from residents of California. Compliance is not optional compliance is required and can cost you up to $7,500 per intentional violation to not comply.
Key Rights Provided Under CCPA.
CCPA is primarily established to give consumers rights over their data. A closer examination of rights includes the following:
-
Right to Know Consumers have the right to know what personal information is collected, how it is used, and who it is shared with. This level of transparency is especially important in an era where data is often commercialized.
-
Right to Delete CCPA allows consumers to ask for their personal information to be deleted. There are exceptions to this, of course — for example, when the information is retained in order to complete a transaction, or to comply with other legal obligations such as detecting fraud. Even though there are exceptions, companies are required to take and respond to deletion requests in a timely process.
-
Right to Opt-Out Perhaps one of the most impactful rights in CCPA is the right to opt-out of the sale of personal information. If a business sells consumer data, the business must provide consumers with a clear and conspicuous way to opt-out (e.g. a "Do Not Sell My Personal Information" link on its website).
-
Right to Access Consumers have the right to request a copy of the information we have collected about them in a structured, commonly used, and machine readable format. This allows for easier, "portability" of the consumer's data between services, if desired by the consumer.
-
Right to Non-Discrimination CCPA prohibits businesses from discriminating against the consumer for exercising their rights. A business cannot, for example, refuse service, charge different prices, or provide a different quality of service from the consumer that request deletion of their information or opt-out.

Practical Steps for Indian Businesses to Achieve Compliance with CCPA
Compliance may be difficult, yet it can be simplified with systematic effort. This is how Indian businesses can create a plan:
1. Conduct a Data Audit
Your first goal is to identify what personal data you collect, where and how it is stored, and how and with whom it is shared. This audit is our jumping-off point for compliance.
2. Revise Privacy Policies
Your privacy policy must explain the ways in which you collect, process, and share consumer data. You can also issue information to consumers on how to assert their rights under the CCPA.
3. Provide Access and Deletion Options
Consumers must also have easy access to request their data or request deletion. Automating these processes allows you to avoid errors and mitigate the consequences of the deleting process.
4. Train Employees
Employees should know the CCPA, the importance of data privacy, and how to address consumer requests. Training sessions can also ensure that employees do not forget these fundamentals and inadvertently create a breach.
5. Monitor Third-Party Vendors
If your business shares data with vendors or contractors, your organization should ensure that those vendors or contractors are also CCPA compliant when it comes to the control of consumer personal information. If you contract with a vendor or contractor who has contact with consumers' personal information, your contract should require that the vendor or contractor follow CCPA guidelines.
6. Keep Records
Maintain records of consumer requests and your responses to those requests. This can be useful for any audits or inquiries that could take place to verify compliance.

Implication of Non-Compliance
Not complying with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is not only a legal issue, but it can leading to serious financial, operational, and reputational impacts on a business. Businesses may want to ignore the CCPA, especially if they do not operate from within California, but the implications will reverberate well beyond the original act of ignoring CCPA. Below, we will discuss in detail the implications listed 1. Fines The CCPA allows regulators to issue fines for failure to comply with the law’s requirements. The monetary amounts associated vary depending upon the nature of the violation. Unintentional Violations: A business that commits an inadvertent violation can be fined up to $2,500 for the violation. Even if the wrongful act occurred unintentionally, they can become sizeable numbers quickly. Intentional Violations: A business that intentionally and/or knowingly fails to comply or ignores a consumer’s rights, they may be subject to a fine of up to 7,500 per violation.
Litigation
The CCPA gives consumers the right to bring a lawsuit for private rights of action in certain cases, especially if there is a breach regarding personal data. This includes data being stolen, accessed without authority, or disclosed.
Individual lawsuits: If an individual consumer is affected, they are entitled to sue the company for $100-$750 per incident, or actual damages, whichever is higher.
Class Actions: If multiple consumers are impacted, litigation could turn into a class-action lawsuit and become immensely costly for settlements and lawyer expenditures, costing the company in the millions.
The idea is that a small violation of the law, like not deleting a consumer's data after being asked to delete it, could find the company litigating in a lawsuit that drains resources and dedicate even more time to deal with a single violation.
Loss of Customer Trust
In the Internet age we live in today, trust is a company’s most valuable asset. A failure to protect consumers’ privacy or comply with CCPA can have serious consequences for a brand’s reputation.
Consumers are increasingly educated about their rights and more willing to switch to competing companies when they believe their data isn’t handled appropriately.
Additionally, unfavorable news spreads via social media platforms and news publications, compounding the damage to a brand’s reputation.
Trust is an essential component of any relationship, including partnerships, and loss of customer trust may have consequences for partnerships, as distrust in an organization’s privacy practices may cause hesitation to partner with that organization.
Operational Disruption
There are a variety of ways that non-compliance may disrupt operations of your organization:
Emergency Remediation: Once a compliance issue arises due to a violation, rectifying that situation can be time consuming and costly. Depending on the severity of the violation, consulting with an expert in the field, investing in new technology, or even redesigning processes and practices may be necessary.
Resource Drain: In addition to the monetary costs that may be incurred, time and expertise are used up responding to violation issues where time and expertise might otherwise be directed toward innovation or business growth.
Business Interruption: In the most extreme case, regulators may suspend operations entirely, or conduct an audit that will halt operations, both of which disrupt revenue and erode customer service abilities.
Being proactive with compliance allows organizations to embed privacy practices and uphold comfort with being compliant—being in compliance lowers the risk of disruption.
The Future of CCPA and Global Data
Privacy Trends CCPA is part of a global trend toward stronger data protection. Other laws, such as the GDPR, India's proposed Data Protection Bill, and other state laws indicate privacy is on a universal priority list. While CCPA creates headaches for some Indian businesses, it creates an opportunity to: Instill trustworthiness with clients globally. Improve governance practices with respect to data. Differentiate from competitors by demonstrating commitment to a priority of privacy. The proactive compliance initiatives can be a selling point in a market that is gradually awakening to the importance of data security.









































