Can Students Lose Their Data When Using AI Tools?

Introduction
The education system has been revolutionized by artificial intelligence. Feedback on their essays with an instant response, adaptive exam where the level of complexity depends on the performance of the student or even computer marked essays are some features that has lightened teachers and students workload in classes by hours. But the progression of AI technology requires some sober thinking about ensuring privacy in individuals' and scholars' data. AI Applications Can Be Powerful And Tailored .But the development of AI technology demands serious reflection in regards to guaranteeing the privacy of personal and academic data. AI solutions can be effective and customized to the individual but carry the drawback of harvesting, processing, and storing personal information sometimes even without the explicit consent of the user. It is crucial for students to learn about practices like these and related risks in order to stay in command of their online identity and academic integrity.
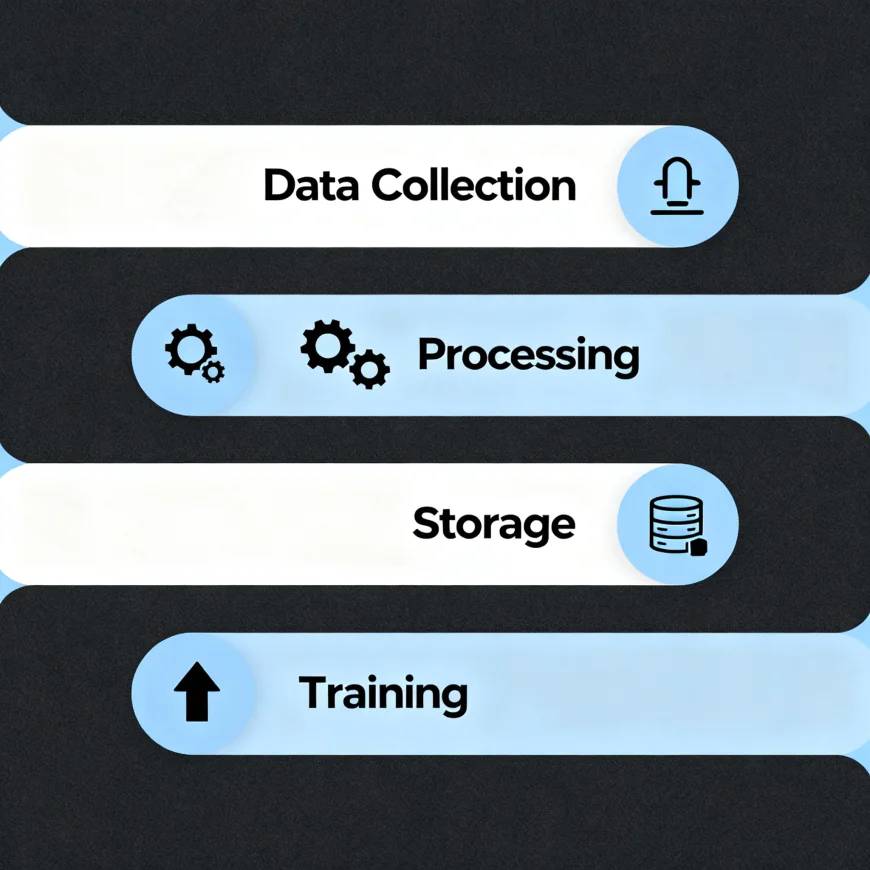
The AI Tool Workflow: Four Main Steps
Whenever an AI service is used, be it a chatbot, a grading tool, or a search engine, the process goes through a basic four step cycle in every instance:
Data collection
This is representative of the input stage. Asking a question in ChatGPT or uploading a document to Turnitin or submitting an assignment to Google Classroom is providing data which the system accepts, right away. This begins the entire process.
Processing and Analysis
The instant that data is received, the AI model will start working.
In the case of chatbots, the system applies its large language models to decompose the text, establish the context, and then come up with a suitable response. For the instance of online learning sites, it employs a sequence of algorithms to review the input for example, marking an exam, plagiarism detection in an essay and/or suggesting personalized study notes.
Storage
This is the final, infinite loop. Many AI services exist to become increasingly efficient as the time goes on and it picks up what it learns from the user's interactions.
Most commonly, the system uses anonymized user data (the type of which has personal identifiers stripped off) to train and hone its fundamental models in a sustained way.
It becomes more accurate and efficient through this process of ongoing training. On the other hand, it requires careful cleaning of data so as not to inadvertently carry over and transfer sensitive data in the new model.
Training and Improvement
This is the last, unending loop . A lot of AI services are there to get more efficient as the time passes and they learn from the user's interactions.
Over all, the system uses anonymized user data (data that had personal identifiers stripped off) toconstantly train and improve its root models.
Performance and accuracy of the tool get enhanced due to this ongoing training procedure. But it requires careful data cleaning so that you don't pass and carry sensitive data to the new model inadvertently.
Types of Student Data Collected by AI Tools
User Input (The "What You insert")
User Input is the easiest data collection, and it encompasses all that you actively paste, type, or upload into the system. It reflects the raw information and content provided by the student to complete an assignment.
Content: These can be essays in draft form, homework problems and solutions, project documents, and even class notes or personal thoughts if they are typed onto an AI chatbot interface.
The Risk: This information is generated by the user in a less structured manner and as such usually includes very sensitive data. A student may copy personal data such as their medical conditions or confidential research into these machines, and that specific information may end up being saved and potentially utilized for AI model improvement later on, which would be a significant privacy risk.
Account Information
Account Information is the traditional identity set with which to register and authenticate and it ensures that the platform identifies the user creating the connection to the service.
Identity Information: Typical information that gets stored includes your full name, e mail address, student identification number, and any other school identification.
Context: In addition to that, sites also collect class Enrollment data and user roles (e.g., student, teacher,etc). This data is primarily used in authenticating user and in personalizing dashboards and learning paths (you end up with the correct assignment and course materials.)

Behavioral Data (The "How You Use It")
Data behavoral tracks the interaction of a pupil with the site. This is very important for AI platforms to adapt the learning experiences and give personalized recommendations. Metrics of Interaction : These consist of Session lengths (the time spent on a lesson), Click patterns (the menus or features clicked the most), and individual Performance metrics. Insights: Performance metrics are quiz scores, completion time for assignments, and progress trends. This kind of behavioral intelligence is an incredibly powerful way of personalization in education but it can also unintentionally expose a student's studying patterns, alertness or even difficulties with course work which some students might want to keep private.
Assignments and Submissions
The student has produced all the items, the documents, files, and data tables that were finished and turned in to the site legally. Repository Content: The platform will have all the files uploaded, whether they are essays, quizzes, spreadsheets, code files, or multimedia projects, in its repository. The Persistence: At times, this archive is in place forever. For instance, there are some software programs like Turnitin that keep the submitted work in their database for future retrieval purposes when conducting plagiarism checks.
Access Risks: Besides being unremovable, such data is always available to the school managers, teaching aides, or professors. Moreover, there is a chance that these highly valuable academic records may be unintentionally exposed in case the platform's security settings or access controls are not functioning properly.
Technical and Operational Risks in AI Education Tools AI in software has different levels, but simultaneously, it manifests significant risks and factors that could disrupt students' learning and impact the data. All these risks can be categorized into four main groups: Technical Failures and Server Crash Even the largest cloud providers experience occasional interruptions. A technical failure in an AI service that lacks good and superfluous backup systems will lead to the following:
Privacy Policies and Data Sharing
Usually, legal documents referring to these products point out the least of the privacy risks as follows: Over control: The regulations could require the data to be kept for educational purposes for a time that would be totally unnecessary and thereby exceedingly long. Third Party Sharing: Sharing data with third parties consisting of research partners, advertising companies and even analytics firms are some of the agreements that have clauses in them. Consequently, the number of organizations that can access a student's data has grown enormously. Limited Deletion: Consumers may think that their control over the erasure of their data from the system is minimal or non-existent once it is uploaded. Furthermore, there is a very large disparity in the extent of adherence to such important regional laws as FERPA in the U.S. or GDPR in Europe, which mainly serve to protect against the disclosure of student records, among the different providers.
Keep Your Private Info, Private
Don't share your real world identities. When you're requesting assistance on call, in a chat, or even in an e mail, never provide:- Your full, real name. Use a nickname or simply your first name, such as "Alex B." Your home address or phone number. Any ID numbers such as your student ID.

Always Have a Backup Plan
Cloud is Essential:
Take advantage of Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive. They will save what you do and retain older copies, so even if you get into trouble and erase something important, you will still have it.
Local Copy Also: Maintain local copy of critical paper on your laptop or external hard drive. Incorporate a date time into the file name so you'll know which one is the newer version, and you could always roll back to an older version in case you botch the newest version.For Coders Whenever you do any coding or big text project, utilize something like git. It is your file's personal time machine, which maintains a record of all changes you and other make in complete security.
Balancing Convenience and Security
The undeniable benefits of AI tools consist of customized teaching, instant feedback, and seamless cooperation. However, these advantages have to be balanced against the possible loss of privacy of data. Through strong digital hygiene like backups, careful data sharing, and selective tool usage, students will be able to make use of AI for learning without compromising their personal or academic information.
Conclusion
The students' ways of learning, interacting, and even producing have been revolutionized by AI based learning software. But along with great power there is also the great responsibility that comes with it. Students are able to do everything from knowing data streams to putting preventive security measures in place and thus they hold the keys to the safety of their online traces. To be aware of possible vulnerabilities, to follow best practices, and to consult campus IT professionals, students will be able to use AI advantages without fear of information being leaked. In a technology pervaded world, educated awareness is the students' strongest weapon.