10 Hidden DevSecOps Misconfigurations That Can Sink Your Cloud Security
DevSecOps aims to embed security into every step of the DevOps pipeline — but even the best intentions can be derailed by subtle misconfigurations. In this blog, we expose 10 hidden DevSecOps pitfalls that could silently sabotage your cloud environment. Whether you're a cloud engineer, DevOps lead, or security professional, understanding these risks is crucial to maintaining a secure, compliant, and resilient infrastructure. Learn how to identify, avoid, and remediate these critical flaws before they become entry

1. Overly Permissive IAM Roles
The Misconfiguration:
Granting cloud services or users wildcard (*) permissions instead of least-privilege roles.
Real-World Impact:
In 2021, a misconfigured IAM policy allowed an attacker to escalate privileges in a cloud environment and exfiltrate data from an S3 bucket.
What to Do:
- Avoid using * in IAM policies.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC).
- Regularly audit IAM permissions using tools like AWS IAM Access Analyzer or GCP Policy Analyzer.
2. Unscanned or Vulnerable Container Images
The Misconfiguration:
Using Docker images from public repositories without scanning them for vulnerabilities.
Real-World Impact:
A fintech company unknowingly deployed a container image with a known Log4j vulnerability — leading to full system compromise.
What to Do:
- Use trusted base images only.
- Integrate container scanning tools like Trivy, Clair, or Anchore into your CI/CD pipeline.
- Automate re-scans with each update.
3. Secrets Stored in Plaintext
The Misconfiguration:
Hardcoding secrets, passwords, or API keys in source code or config files.
Real-World Impact:
In 2020, an exposed GitHub repo revealed AWS keys — attackers used them to spin up mining rigs, costing the company $45,000 overnight.
What to Do:
- Use secret management tools like HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, or Doppler.
- Never commit .env or config files with secrets to version control.
- Enable automatic key rotation policies.
4. Poorly Configured CI/CD Pipelines
The Misconfiguration:
Running CI/CD jobs with excessive privileges or without sandboxing.
Real-World Impact:
Attackers compromised a GitHub Actions pipeline and used elevated permissions to inject malicious code into production.
What to Do:
- Run jobs in isolated containers.
- Limit what jobs can access.
- Use signed commits and signed artifacts.
5. No Validation in Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC)
The Misconfiguration:
Deploying IaC (like Terraform, CloudFormation) without validating for security flaws.
Real-World Impact:
One company accidentally exposed an entire cloud VPC to the internet due to a wrong CIDR block in their IaC template.
What to Do:
- Use tools like Checkov, TFLint, or CloudFormation Guard to scan IaC templates.
- Enforce code reviews and automated security checks.
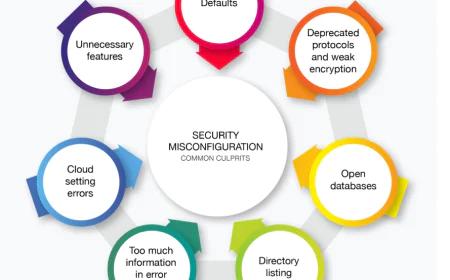
6. Public Cloud Storage Buckets
The Misconfiguration:
Leaving cloud storage (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Blob) publicly accessible by default.
Real-World Impact:
A marketing firm exposed 500,000 customer records by misconfiguring an S3 bucket.
What to Do:
- Block public access at the account level.
- Use bucket policies and ACLs wisely.
- Use tools like AWS Macie or GCP Cloud DLP to detect exposed data.
7. Unpatched Dependencies
The Misconfiguration:
Not scanning or updating dependencies and libraries regularly.
Real-World Impact:
Equifax’s massive breach was caused by a known vulnerability in Apache Struts that went unpatched for months.
What to Do:
- Use dependency scanning tools like Snyk, Dependabot, or OWASP Dependency-Check.
- Set automated update policies for critical patches.
8. Lack of Security Testing in CI/CD
The Misconfiguration:
Skipping security tests in the pipeline due to speed or complexity concerns.
Real-World Impact:
A healthcare app pushed an update without security validation. It introduced an XSS vulnerability, leaking patient data.
What to Do:
- Integrate SAST (Static Application Security Testing) and DAST (Dynamic) in the CI/CD pipeline.
- Use lightweight tools like SonarQube, Bandit, or OWASP ZAP.
9. Misconfigured Firewalls and Security Groups
The Misconfiguration:
Allowing broad inbound/outbound traffic in cloud firewall rules or security groups.
Real-World Impact:
A misconfigured security group exposed an internal database to the public internet, which was then indexed by Shodan.
What to Do:
- Follow the principle of least access for network rules.
- Use tools like CloudMapper or Prowler to audit your security groups.
10. No Monitoring or Alerting for Anomalies
The Misconfiguration:
Lack of centralized logging, threat detection, or alerting.
Real-World Impact:
A SaaS company didn’t notice a compromised developer account for weeks because no alerts were configured.
What to Do:
- Use centralized log aggregation (e.g., ELK, Datadog, or CloudWatch Logs).
- Enable anomaly detection and alerts for suspicious activity.
- Set up SIEM tools or cloud-native solutions like AWS GuardDuty, Azure Defender, or GCP Security Command Center.
DevSecOps isn’t just about plugging in a few security tools — it’s a mindset. Misconfigurations are the silent killers of cloud security, and many slip through the cracks due to automation, speed, or lack of visibility.
But the good news? With the right practices, tools, and awareness, you can catch and fix these issues before attackers do.
- Start with small improvements.
- Automate scans.
- Educate your teams.
- And always assume something could go wrong — because eventually, it will.