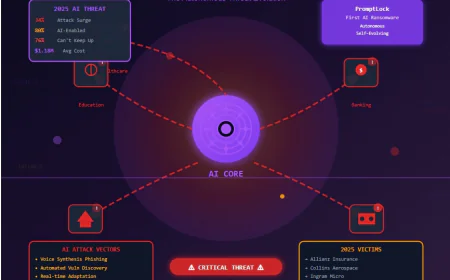
AI & Security: Revolutionizing Cybersecurity in the Digital Age

Artificial intelligence (AI) is turning out to be the biggest game changer in the defense against cyber attacks. It allows firms to move security postures from reactive to proactive. Thus, organizations can predict, detect, and mitigate cyber risks more efficiently. In this article, we will be discussing the deep integration of AI into cybersecurity strategies, the advantages, the main use cases, the obstacles, and the future of AI in cybersecurity.
Understanding AI in Cybersecurity
AI denotes the use of technology that employs ML, NLP, and behavioral analytics to process large amounts of data, detect patterns, and reach decisions with little to no human involvement. In this regard, AI-driven systems in cybersecurity are looking at different sources like network communications, user actions and computer logs to find signs of cyber incidents.
AI has come a long way from traditional cybersecurity approaches that relied on fixed signatures and rules. Moreover, it has been continuously adapting to newer threats, thereby becoming markedly more so. This feature of AI-powered solutions allows them to pinpoint new malware, zero-day vulnerabilities, insider threats, and other subtle cyber risks at once.
The Critical Role of AI in Cybersecurity Operations
The use of AI in cybersecurity has come to dominate in many places due to the following:
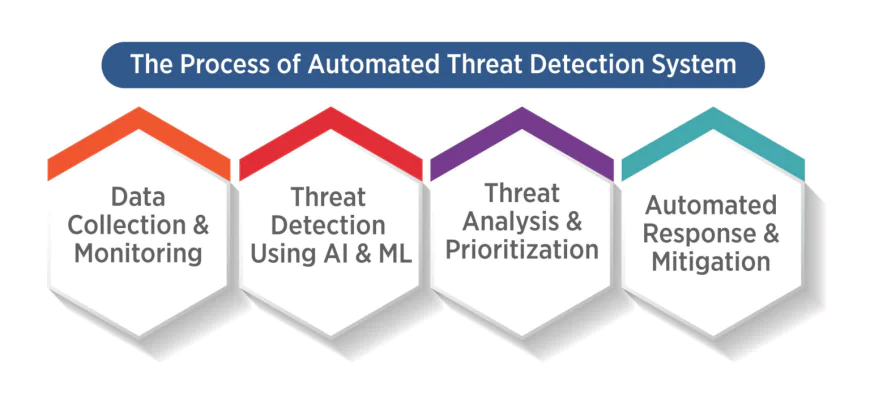
Automated Threat Detection and Anomaly Monitoring: Artificial Intelligence observes users, networks, and devices to learn what is normal and then throws up a red flag as soon as there is a deviation from the norm. A case in point is Darktrace’s ActiveAI platform which has given firms like Aviso-a financial institution that operates with an awesome $140 billion in assets-the capability to be proactive in understanding threats by automatically examining millions of network events and also preventing thousands of malicious emails that were not picked up by legacy systems.
Advanced Malware Identification: Traditional antivirus software sticks to the methods of virus signatures that have been disclosed, but AI-based malware detectors not only go through the signature-less files but also examine the attributes of each file, process behaviors, and memory usage to tell if that is a new or morphing malware variant. CordenPharma, a global pharmaceutical producer, installed a self-learning AI that was adept at detecting silent crypto-mining malware which had escaped classical defenses, thus, data exfiltration was stopped and sensitive IP got protection.
Identity Protection and Account Takeover (ATO) Prevention: AI evaluates access patterns, including login patterns, device fingerprints, and contextual factors, such as geographical irregularities. One of the major global banks had to cope with a tide of ATO cases and they turned to Memcyco’s AI platform for real-time phishing site detection, user alerts, and feeding decoy data to the criminals that resulted in a whopping 65% cut in the number of fraudulently compromised accounts.
Behavioral Threat Hunting: AI is on standby, keeping an eye not only on the users but also on the network traffic, all the time hunting for the next newcomer that is likely to be a threat by associating it with insiders or poor credentials. It is this processing capacity of AI to deal with vast amounts and very complex data that speeds up the uncovering of very little signs of compromise.
Addressing Modern Cybersecurity Challenges with AI
Increasingly more cloud services, IoT devices, and mobile endpoints are parts of the same network, and thus are exposing organizations to a lot of risks in the security area.
Also, cybersecurity teams' main problems include:
1. Cyberattacks have gone so far that now they are creating very complicated situations and are also able to adapt their tactics to each defense strategy. Such adversaries would, therefore, require defense mechanisms that are equally dynamic.
2. An enormous amount of data is produced from logs, network events, and endpoints-billions of data points that need to be analyzed very quickly so that the risks can be identified.
3. A shortage of cybersecurity specialists is making it hard to detect and respond to threats in time.
4. Security analysts are getting thousands of alerts daily, out of which, most are false alarms.
Artificial Intelligence takes on these hurdles by being patient and persistent with the data, picking only the important alerts, ridding the team of performing monotonous tasks, and sharing the knowledge with the human experts, thus enabling the teams to focus on the truly urgent threats.
Real-World Case Studies of AI in Cybersecurity
Darktrace and Aviso: The AI of Darktrace was able to recognize such anomalies as peculiar data transfers and it also stopped 18,000 malwares-email in the network of Aviso that traditional tools were not able to detect. The AI was allowed to look into 23 million events and to highlight 73 as the most important alerts thus, considerably lowering the workload of the analysts. This whole process has made Aviso to give more time and resources on the strategic security improvements and compliance.
CordenPharma: CordenPharma used AI to dynamically baseline user and device behavior in order to deal with the stealthy malware and supply chain threats. The AI picked up the crypto-mining malware that was communicating with dubious endpoints and it also stopped the leakage of data which is an example of the AI’s capability to safeguard important healthcare and pharmaceuticals data.
Memcyco in Banking: A worldwide bank that was significantly hurt by the expensive ATO attacks decided to utilize the Memcyco's AI-enabled platform which tracked the phishing sites and notified the users instantly. The system also replaced the compromised credentials with that of the decoy data so that ATO cases were reduced by 65% and millions in potential fraud losses were saved.
IBM Watson for Cybersecurity: IBM Watson augments cybersecurity staff by linking global threat intelligence with internal security data to reveal the paths of emerging phishing campaigns or malware attacks. The application in finance resulted in the early blocking of advanced phishing attacks, thus, protecting the privacy of financial client data.
Advantages of using Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
Prompt Incident Management: Through automating and prioritizing, AI measures the time to detect and respond incidents from days or hours to minutes.
Higher Detection Accuracy: Smart algorithms can spot new and advanced attacks which signature-based tools might not even be aware of.
Increased Capacity and Efficiency: AI can monitor big amounts of data which no human could do.
Fewer False Alarms: Analyzing behavior in context helps to eliminate irrelevant alerts and thus lessens the fatigue from alerts.
Cost Saving: Automation helps to meet the shortage of skilled workers and at the same time, it lowers the operational costs.
Difficulties and Factors to be considered
Adversarial AI: Security experts have to deal with hackers who are trying to trick or contaminate AI models, so they need to come up with very solid defense systems.
Explainability: Making AI's decision process clear is essential for the establishment of trust and legal adherence.
Privacy: It is very important to find a suitable point between user data privacy regulations and the effectiveness of threat detection.
Integration Complexity: In order to achieve the highest efficacy, AI tools need to be integrated with the current IT and security infrastructures.
Future Outlook: AI, the first line of defense, and the enemy in cyberspace
AI will play a dual role where it will not only defend but also be a weapon in the battle of cybersecurity. On one hand, the use of AI in cyberattacks has been continuously increasing which on the other hand, is stimulating the development of AI-based defense mechanisms. AI's integration with cloud, IoT security, and automated response systems will continue to expand, thus creating defense ecosystems that are adaptive and resilient. Although human cybersecurity specialists will still be of great importance, the power of analysis and automation provided by AI will be a great support.
AI is a revolutionary factor in cybersecurity, turning the traditional defensive strategies from reactive to predictive ones which means the companies are always one step in front of cybercriminals even in a constantly changing digital environment.