Cal.com Authentication Bypass via Bad TOTP + Password Checks
Critical 2FA vulnerability in next-auth allows attackers to bypass password checks using TOTP codes. Learn how flawed authentication logic exposes user accounts and how to fix it.

Summary
In case an attacker presents a TOTP code, they will be able to bypass password checking and unlawfully access user accounts. The authentication procedure has poor conditional logic, and this is the reason for the issue.
Details
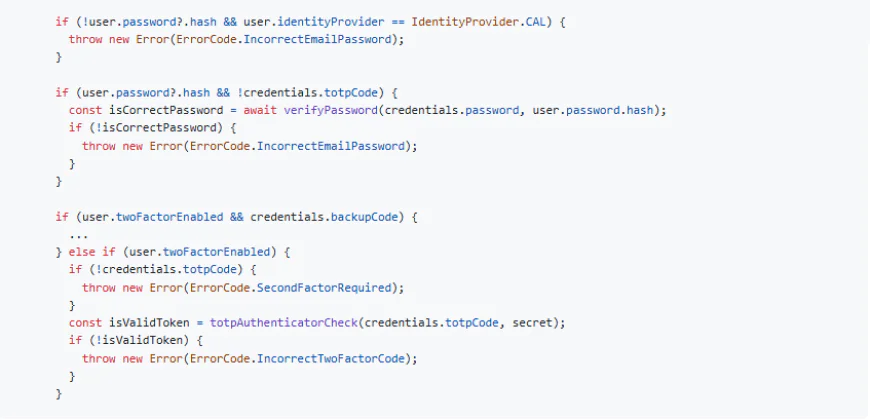
The gap in security resides in the authorise() function of the credentials provider. The location of its occurrence is in the directory packages/features/auth/lib/next-auth-options.ts. The flaw in the authentication on lines 179–187 is the most critical part. In the case where a TOTP code is provided, it simply bypasses the password check no matter if other criteria are satisfied. Consequently, this gives rise to two separate issues:
Scenario 1 - Bypass for Non-2FA Users
If an assailant enters a non-null value in the totpCode field, the password authentication is bypassed since the logic yields false when the totpCode is there. This scenario concerns the users who do not have 2FA activated (the majority), allowing the attackers to sneak past both password and TOTP validation. On top of that, the function mistakenly continues to authenticate the user without applying any further verification.
Scenario 2 - Reduced Security for 2FA Users
The presence of a totpCode makes the function skip password verification, which makes the multi-factor authentication process less secure, even for users who have 2FA turned on. The TOTP code is checked, but not the password, which means that the account could be hacked if someone knows the TOTP code.
Vulnerable Code
packages/features/auth/lib/next-auth-options.ts:175-243
Potential Attack Method
In some cases, giving someone a totpCode and their email address could let them in without having to enter a password. Even if this code is wrong, attackers can still get into accounts that don't have 2FA or get around the password check for 2FA users.
Impact
This flaw could let people who shouldn't have access to sensitive user data, like calendars, meeting links, and personal information. Without 2FA, attackers could get in just by knowing the victim's email address, which makes the attack easier to carry out. Even if users have two-factor authentication (2FA) turned on, the hacked system lets attackers get around one of the authentication factors, which makes security weaker. Also, the flaw could be used to enumerate and impersonate users, which would let attackers get into any account if they have the right permissions.
This vulnerability can be lessened by changing the way the system checks the password and the TOTP code (if necessary) to make sure they are both correct.