Chaos Engineering in Kubernetes: Breaking Things to Make Them Stronger
Modern applications run on fast, complex Kubernetes clusters — but what happens when the unexpected strikes? Chaos Engineering is the bold practice of intentionally breaking systems to uncover weaknesses before they cause real damage. From deleting pods to simulating node failures and network outages, chaos experiments help teams prove their systems can withstand the worst. In this blog, we’ll explore how Chaos Engineering is making Kubernetes environments more resilient, reliable, and production-ready in 2025, along with tools and real-world practices you can apply today.

Introduction
Cloud-native applications are fast, scalable, and dynamic — but failures are inevitable. Even with Kubernetes as a strong orchestrator, what happens if a pod crashes? Or if a node suddenly goes offline?
That’s where Chaos Engineering comes in — a practice where you intentionally break your systems in controlled ways to uncover weaknesses and build resilience.

What is Chaos Engineering?
Chaos Engineering is the discipline of:
“Deliberately injecting failures into systems to test resilience.”
These failures can include:
- Pod crashes
- Node shutdowns
- Network delays or partitions
- API latency injections
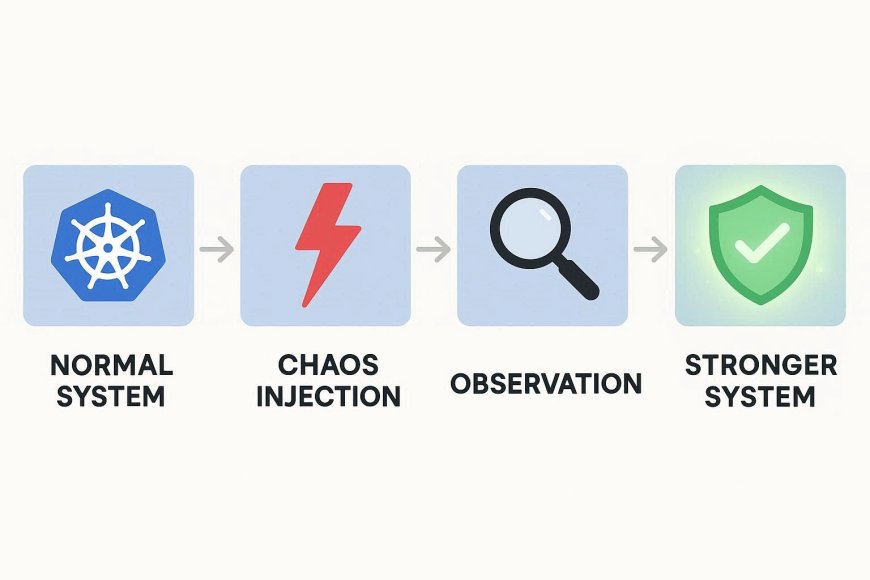
Why Chaos Engineering in Kubernetes?
Kubernetes thrives in dynamic, distributed environments — which makes failures natural:
- Container crashes
- Unavailable nodes
- Network issues
- Misconfigured policies
By running chaos experiments, teams can:
- Discover hidden weak points
- Validate self-healing and failover
- Improve incident response
- Prepare for real-world outages before they happen
Popular Chaos Engineering Tools for Kubernetes
- LitmusChaos – CNCF project, highly extensible chaos framework.
- Chaos Mesh – Cloud-native with scheduling & visualization support.
- Gremlin – Enterprise SaaS platform for chaos engineering.
- PowerfulSeal – Python-based tool designed for Kubernetes.
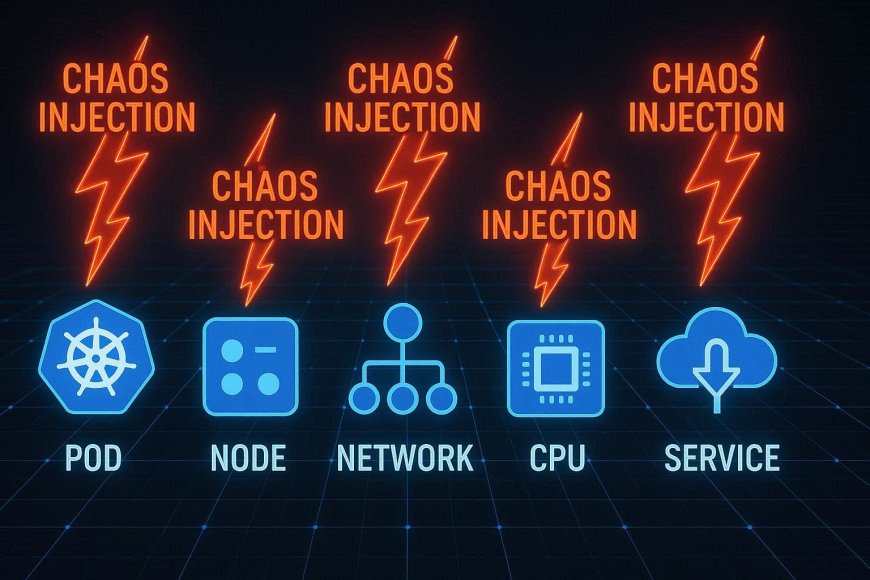
Common Chaos Experiments in Kubernetes
- Pod Delete → Randomly delete pods to test recovery.
- Node Failure → Simulate a node crash to test workload redistribution.
- Network Latency → Delay or block traffic to test service resilience.
- CPU/Memory Stress → Introduce resource overloads.
- Service Kill → Shut down critical services to test dependencies.
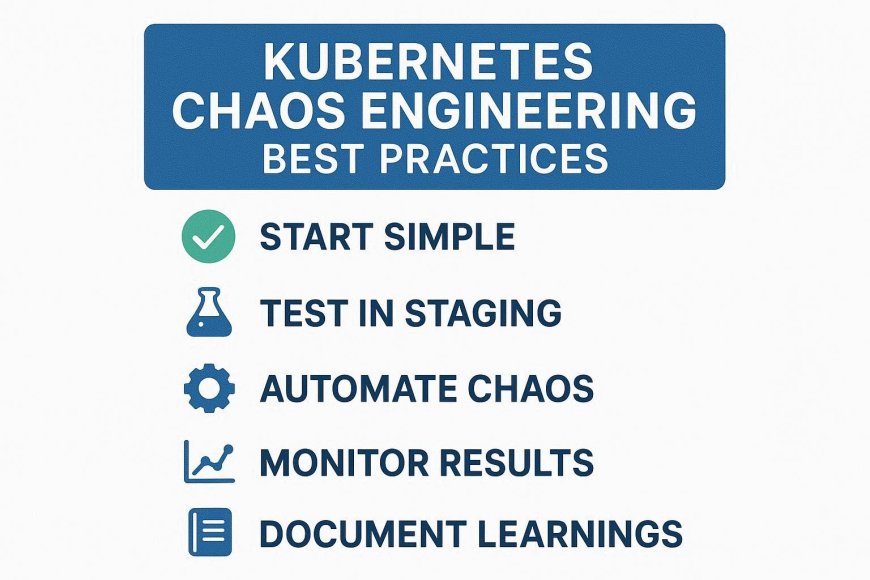
Best Practices for Chaos Engineering in Kubernetes
Start with simple experiments (like pod deletion)
Run in staging before production
Define a steady state (expected behavior)
Automate chaos within CI/CD pipelines
Monitor with Prometheus, Grafana, or Datadog
Document results and update incident playbooks
Real-World Example
An e-commerce company applied chaos experiments:
- Simulated pod deletions and network latency
- Verified that the checkout service recovered properly
- Identified a load balancer misconfiguration
- Avoided potential downtime during peak hours
Conclusion
Chaos Engineering helps teams make Kubernetes environments battle-tested.
Instead of waiting for systems to fail, break them on your terms — and build stronger, more resilient platforms.