OpenAI Introduces Aardvark, a GPT-5 guy who sifts through your codes to hunt down vulnerabilities-and solve them : A significant shift now implemented in the world of DevSecOps
OpenAI has unveiled Aardvark, an autonomous GPT-5-powered “agentic security researcher” that scans, validates, and patches code vulnerabilities in real time. It marks a major leap in AI-driven DevSecOps, promising faster, more accurate security management across software development. Early tests show strong results, positioning Aardvark as a key player in the growing field of automated vulnerability detection and remediation.

SAN FRANCISCO - A highly significant affair has transpired which is attracting a lot of interest from the cybersecurity community as well as the software development industry. OpenAI has rendered Aardvark, an "agentic security researcher" that utilizes the company's top-tier GPT-5 large language model, an autonomous instrument. This ground-breaking device signifies a major transformation in the vulnerability detection and patching management at scale of companies, thus, it is artificial intelligence that will play a vital role in modern software development security practices.
The Rise of AI-Powered Security Research
The unveiling of Aardvark is a noted turning point in today’s security reports and it is indeed the very AI that keeps on changing the way different people like developers and security teams cope with code vulnerabilities. Instead of the signature-based detection method which is the usual CSR of most conventional security scanning tools, Aardvark deploys the cutting-edge reasoning abilities of GPT-5, which effectively mimics the human security experts who are capable of locating, understanding, and automatically patching the code vulnerabilities not just in a specific software but all the way to the entire software repository.
Aardvark that is only in private beta testing at this point, is designed to be a blessing to the developer and security teams by making their efforts in vulnerability identification and remediation a hundred times more effective. The announcement from OpenAI mentions the agent's ability to "perpetually scrutinize source code repositories to uncover weaknesses, measure exploitable condition, categorize with severity, and suggest precise patches." Such an all-round strategy is the next mile marker in the journey of automated code security as it addresses one of the riskiest pain points in the DevSecOps workflows of the day.
How Aardvark Works: A Multi-Layered Approach to Code Security
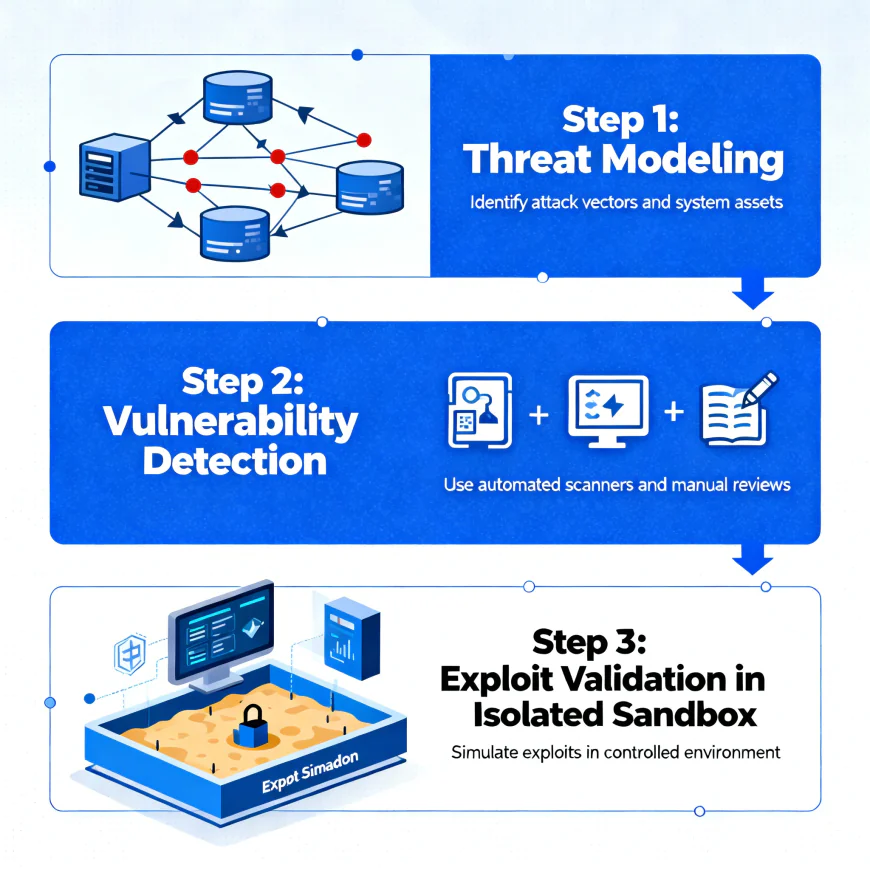
The operations of Aardvark give you an understanding of its influence on the health of hacker news discussion and the whole cybersecurity communitys' attention given to the tool. The agent introduces itself as a protective cop by getting into the software development channel and keeping watch on every commit and code change that happens in the repository.
The mechanism behind it is a complex one that takes a multi-step approach starting from analyzing the entire source code domain thoroughly. It first digs deep into every bit of the project's codebase to generate what it terms as a "threat model" - a strategic representation showing the main security concerns of the software and the architecture. With this basis, the agent will be able to keep its context all through the scanning process which is important to tell apart false positives from real security threats.
The moment this threat model is built, Aardvark ascends the ladder of a project's timeline to uncover the already existing bugs systematically while at the same time monitoring the new changes coming in to discover the new security problems. The true creation of Aardvark is in the following step: when a security defect is spot on, the agent will try to bring it out in a detached, controlled, and that is unexploitable area. This validation of the exploit step is of crucial importance as it has to determine whether a weakness is merely a theoretical one and thus not scary, or whether it is one that can be easily exploited causing real-world hazards.
GPT-5: The Powerhouse Behind Aardvark's Intelligence
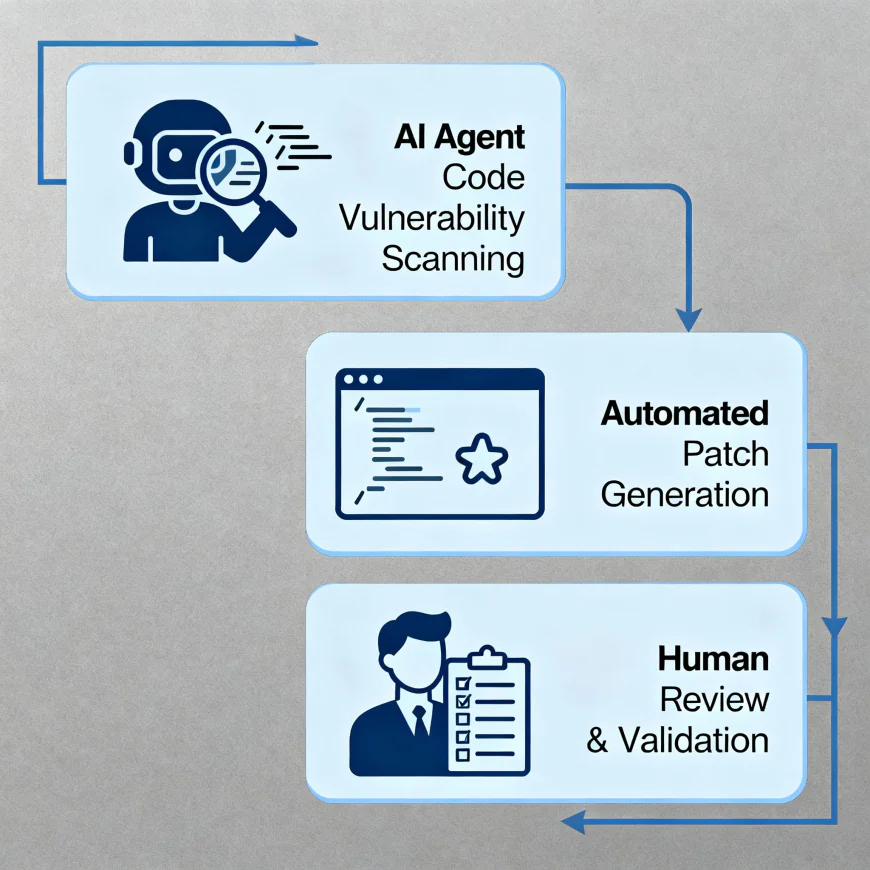
Aardvark's effectiveness is wholly reliant on OpenAI's GPT-5 model which was launched in August 2025. The firm has praised GPT-5 calling it a "smart and the efficient model" now being endowed with the deeper reasoning capability and thus, making GPT-5's thought process more creative and also having a "real-time router" that can choose the best-suited model based on the conversation type, complexity, and user intent.
This tech complexity implicates that Aardvark is not a universal code analyzer. Instead, it constantly tailors its analytical structure to the peculiarities of each codebase resulting in more accurate vulnerability detection and more appropriately fitting patch suggestions. After the exploitability is determined, the system employs OpenAI Codex, its particular coding agent, to generate patches that focus on the vulnerabilities that have already been identified - those patches will then be submitted for human analyst review before being implemented.
Real-World Impact and Proven Results
Aardvark has been deployed early, and the results are already significant as they show the agent's ability to handle difficult cybersecurity problems. OpenAI says that the agent's contribution consisted of spotting at least 10 CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) in open-source projects during the testing process. This was achieved in OpenAI's internal code-comparison and external partners, thus proving Aardvark's worth as a tool for finding vulnerabilities.
This feature is quite a boon for both the security teams and the development organizations since it rightly translates into business value. Aardvark not only helps find vulnerabilities but also takes over the discovery and triage process and the initial phases of it. As a result, Aardvark has made a considerable cut in the manual scanning time. Security researchers are now free to direct their efforts towards complex analyses, threat modeling, and strategic security initiatives. In the age of internet security, where experts are still hard to find and the product-development process is speeding up, this advantage of efficiency is considered to be a vital competitive edge.
The Broader Competitive Landscape
Even though Aardvark is a big step forward, OpenAI has to deal with tougher competition in the field of AI security. In the first half of October 2025, Google introduced a tool called CodeMender, which has many features in common with Aardvark, primarily that it can find, fix, and rewrite vulnerable code to stop further breaches. Moreover, Google has hinted at the possibility of partnering with the developers of important open-source projects to apply the patches created by CodeMender, thus acknowledging the importance of open-source software for the global digital infrastructure.
Aardvark, CodeMender, and another application known as XBOW are being increasingly considered as indispensable parts of the ongoing continuous code analysis, exploit validation, and patch generation workflows in modern software development. The blending of AI capabilities among different vendors indicates that we are actually seeing the rise of automated vulnerability management as a minimum expectation across the industry rather than a point of differentiation in terms of competition.
DevSecOps Evolution and Industry Implications
The release of Aardvark is in line with the industry trends that stress DevSecOps - the combination of security practices with the software development lifecycle. The current cybersecurity news portrays the concern about supply chain attacks, zero-day vulnerabilities, and the increasing professionalism of threat actors causing the need for the tools that allow for continuous security validation to grow.
With the introduction of Aardvark and similar tools companies need to foresee the day-to-day protection in the same way as a developer caters for bugs that could be turned into vulnerabilities. OpenAI’s approach leans on what it has termed “defender-first model” – presenting Aardvark as an “autonomous security researcher that cooperates with teams by carrying on on-the-go protection as code evolves.” This doctrine acknowledges that security is not a one-time thing but a process that continues, thus by getting it in the formative stages, validating its ability to be exploited in the real world, and providing very easy paths for remediation, Aardvark allows companies to fortify their security posture without slowing down the development process.
Looking Forward: Democratizing Security Expertise
Aardvark is perhaps one of the most important steps in the direction of common people's access to security expertise. OpenAI openly declared: "We are for the security expertise being available to everyone." This pledge has far-reaching consequences for small enterprises and development teams, who have always been at a disadvantage and unable to afford hiring security experts.
A mainstay of the future cybersecurity scenario would be the use of artificial intelligence and the tools to be released would be the ones that are eventually considered to be the best. In fact, the companies that manage to incorporate AI-powered agents similar to Aardvark into their development processes will be the ones to hold the most power in the market due to their speedy detection and fixing of vulnerabilities, thus, the creation of more reliable and trusted software.
Aardvark's launch along with the announcements of OpenAI's gpt-oss-safeguard models tailored for safety classification tasks are clear indications that the tech giants are aware of the role AI will play in the resolution of modern security issues. It is a sure thing that as these tools become upgraded and widely accessible, AI and humans will have to cooperate for code security with the latter augmenting the former by providing the strategic direction, judgment and oversight, while AI takes care of the analytical part which is usually very demanding.